Boyle’s law calculator Online:
Use our Boyle’s law calculator Online.
Boyle’s law states, Boyle–Mariotte law, or Mariotte’s law formula:
P1/V1 = P2/V2.
The initial and final volumes and pressures of the fixed amount of gas.
Boyle’s law states Definition:
Definition of Boyle’s law states:
Boyle’s law (sometimes referred to as the Boyle–Mariotte law, or Mariotte’s law) is an experimental gas law that describes how the pressure of a gas tends to increase as the volume of the container decreases. A modern statement of Boyle’s law is
Boyle’s law states Definition:
The absolute pressure exerted by a given mass of an ideal gas is inversely proportional to the volume it occupies if the temperature and amount of gas remain unchanged within a closed system.
Boyle’s law examples:
Example 1:
5.00 L the volume of gas is at 860.0 mmHg pressure. What is its volume at standard pressure?
Solution:
1) Boyle’s law equation:
P1V1 = P2V2
2) equation values:
(860.0 mmHg) (5.00 L) = (760.0 mmHg) (x)
3) Multiply the left side and divide (by 760.0 mmHg) to solve for x.
x = 5.65 L (two significant figures)
The pressure units of mmHg will cancel. x is a symbol for an unknown and, technically, does not carry units. So do not write x L for x liters.
Example 2:
8.00 L the volume of gas is at 960.0 mmHg pressure. What volume is obtained when the pressure is 1000 mmHg?
Solution:
1) Boyle’s law equation:
P1V1 = P2V2
2) equation values:
(960.0 mmHg) (8.00 L) = (1000.0 mmHg) (x)
3) Multiply the left side and divide (by 1000.0 mmHg) to solve for x.
x = 7.68 L (two significant figures)
The pressure units of mmHg will cancel. x is a symbol for an unknown and, technically, does not carry units. So do not write x L for x liters.
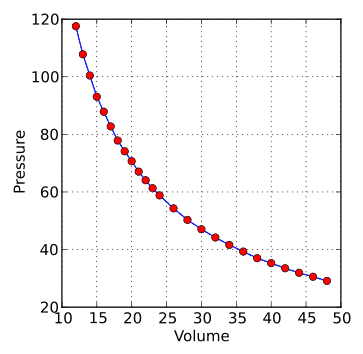
Boyle’s Law Graph:
References:
Gender and Boyle’s Law of Gases