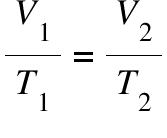Charles’s law Calculator Online:
Use our Charles’s law Calculator Online.
Charles’s law, law of volumes formula:
V1/T1 = V2/T2.
If the temperature increases, the volume of the gas also increases in proportion.
Charles’s law states Definition:
Definition of Charles’s law states:
Charles’s law (also known as the law of volumes) is an experimental gas law that describes how gases tend to expand when heated. A modern statement of Charles’s law is:
When the pressure on a sample of a dry gas is held constant, the Kelvin temperature and the volume will be directly related.
How to do Charles law step by step examples:
Example 1:
5.00 L the volume of gas is at 300 K temperature. What is its volume at 200 K temperature?
Solution:
1) Charles law equation:
V1/T1 = V2/T2
2) equation values:
(300 K) / (5.00 L) = (200 K) / (x)
3) Multiply the left side and divide to solve for x.
x =( (200 K) * (5.00 L) ) / ( 300 K )
x = 3.33 L (two significant figures)
The temperature units of K will cancel. x is a symbol for an unknown and, technically, does not carry units. So do not write x L for x liters.
Example 2:
8.00 L the volume of gas is at 400 K temperature. What is its volume at 200 K temperature?
Solution:
1) Charles law equation:
V1/T1 = V2/T2
2) equation values:
(400 K) / (8.00 L) = (200 K) / (x)
3) Multiply the left side and divide to solve for x.
x =( (200 K) * (8.00 L) ) / ( 400 K )
x = 3.33 L (two significant figures)
The temperature units of K will cancel. x is a symbol for an unknown and, technically, does not carry units. So do not write x L for x liters.