In the last decade the manufacturer developed different types of refrigerants.
The mechanical vapor compression cycle utilizes the evaporation of a refrigerant to absorb the heat, which will lead to lower the temperature of the surrounding of the evaporator.
The first refrigerant used in the word was Ether in 1834 when Perkins proposed a hand operated compressor machine and in 1856 Linde developed a machine working on ammonia.
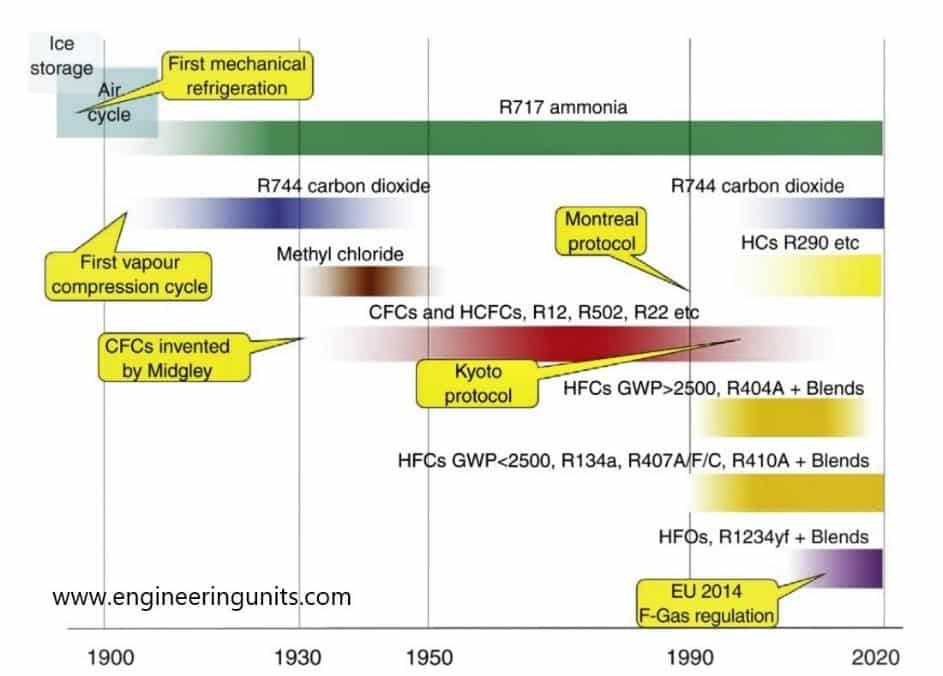
The pace of development was slow until 1930, engineer had only toxic or flammable refrigerants to choose from for their system. Sulphur dioxide, methyl chloride or isobutane used until a new refrigerant known as chloro fluorocarbons or CFCs, which is the fluoro-chloro derivatives of methane, ethane…, called Freon is introduced to the market.
Types of refrigerants
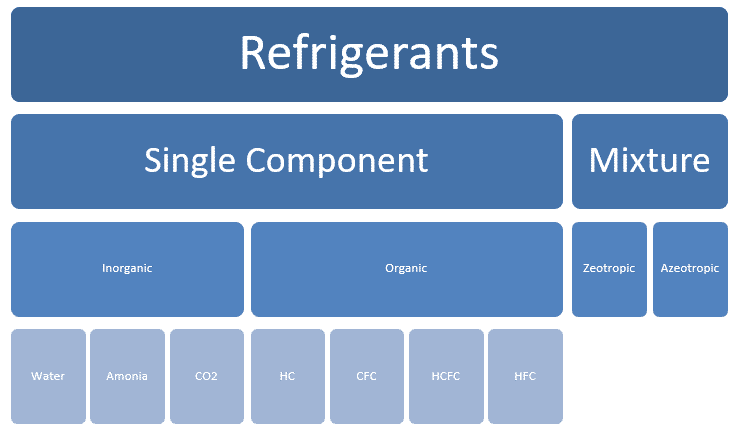
Types of Refrigerants: Simple component
Organic: Some examples
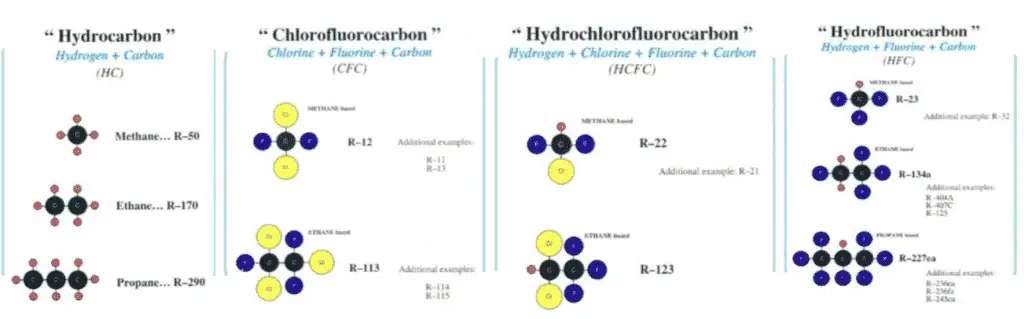
- Hydro-Carbons HC (natural starting molecules from which most refrigerants synthesized) Methane (R-50), Ethane (R-170), Propane (R-290), Butane (R-600) and Pentane (R-601)…
- Chloro-Flouro Carbons (CFC) like Trichlorofluoromethane (R-11), Chlorotrifluoromethane (R-13), Chloropentafluoroethane R-115…
- Hydro Chloro-Flouro Carbons (HCFC) like Dichlorofluoromethane (R-21), Chlorofluoromethane (R-31), Chlorofluoroethane(R-151) …
- Hydro-Fluoro Carbons (HFC), Trifluoropropane (R-263), Difluoropropane (R-272), Fluoropropane(R-281)…
In-organic: Some examples
- Water (R-718)
- Ammonia (R-717).
- CO2 (R-744).
- …
Types of Refrigerants: Blending of refrigerants
Two or more refrigerants blended to achieve the wanted properties:
- Flammability.
- Volumetric Capacity.
- Lower discharge Temp.
Two Types Blending of refrigerants
- Zeotropes.
- Azeotropes.
Types of Refrigerants: Hydrocarbon/ Halocarbons refrigerants:
Hydrocarbon refrigerants
Many hydrocarbon gases used as refrigerants in manufacturing, commercial and domestic applications.
Examples:
- R170, Ethane, C2H6.
- R290 , Propane C3H3.
- R600, Butane, C4H10.
- R600a, Iso-butane, C4H10.
- Blends of the above gases.
Halocarbons
Halocarbon refrigerants synthetically produced and developed as the FREON family of refrigerants.
Examples :
- CFC’s : R11, R12, R113, R114, R115
- HCFC’s : R22, R123
- HFC’s : R134a, R404a, R407c, R410a/,
Atoms in the Molecule per Refrigerants Type:
| Types of Refrigerants | Meaning | Atoms in the Refrigerants Molecule |
| CFC | Chlorofluorocarbon | Cl, F, C |
| CFO | Chlorofluoroolefin | |
| HCFC | Hydrochlorofluorocarbon | H, Cl, F, C |
| HCFO | Hydrochlorofluoroolefin | |
| HFC | Hydrofluorocarbon | H, F, C |
| HFO | Hydrofluoroolefin | |
| HCC | Hydrochlorocarbon | H, Cl, C |
| HCO | Hydrochloroolefin | |
| HC | Hydrocarbon | H, C |
| HO | Hydroolefin (Alkene) | |
| PFC | Perfluorocarbon | F, C |
| PFO | Perfluoroolefin | |
| PCC | Perchlorocarbon | Cl, C |
| PCO | Perchloroolefin | |
| H | Halon/Haloalkane | Br, Cl (in some but not all), F, H (in some but not all), C |
Molecular structures of common refrigerants:
ASHRAE Standards (Number 34):
The number assigned to each refrigerant is related to its chemical composition and the system has been formalized as ASHRAE Standard 34. Broadly, the numbering system is as follows:
- 000 Series Methane Based.
- 100 Series Ethane Based.
- 200 Series Propane Based.
- 300 Series Cyclic Organic Compounds.
- 400 Series Zeotropes.
- 500 Series Azeotropes.
- 600 Series Organic Compounds.
- 700 Series Inorganic Compounds.
- 1000 Series Unsaturated Organic Compounds.
Primary and Secondary Refrigerants
Generally speaking refrigerants are sub-divided into in primary and secondary Refrigerants. A primary refrigerant cools the secondary loop by a heat exchanger.
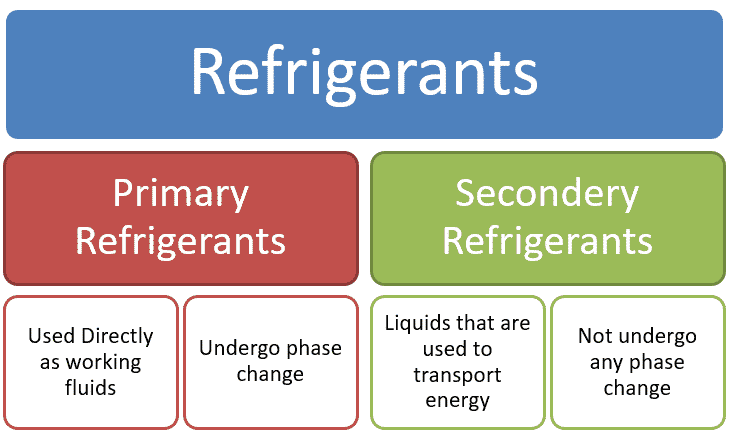
Primary refrigerant used directly in compression (or absorption) system undergo change state and temperature (Compression, Condensation, expansion and evaporation).
Secondary refrigerant used for heat transfer fluid without change in change of state but undergo change in temperature. Secondary refrigerants also known under the name brine’s or antifreeze’s.
Primary refrigerants: The refrigerants are not directly make contact with space to cool known as primary refrigerants
Secondary refrigerants: The refrigerants, which first cooled by primary refrigerants and then used for cooling purpose.
Example primary refrigerants:
- Halocarbon
- hydrpcarbon
- organic compound
- inorganic compound
Example secondary refrigerants:
- Brine
- Water
- Sodium chloride
- Calcium chloride
Common List of refrigerants with ODP and Atmospheric lifetime (year):
| Refregerant Type | ASHARE Number | Chemical Name | Atmospheric Lifetime (years) | ODP |
| CFC | R-11 | Trichlorofluoromethane | 45 | 1 |
| CFC | R-12 | Dichlorodifluoromethane | 100 | 1 |
| CFC | R-13 | Chlorotrifluoromethane | 640 | 1 |
| H | R-12B1 | Bromochlorodifluoromethane | 16 | 7.1 |
| H | R-12B2 | Dibromodifluoromethane | 2.9 | 1.7 |
| HC | R-50 | Methane | 12 ± 3 | <0(smog) |
| HC | R-170 | Ethane | 12 ± 3 | < 0(smog) |
| HC | R-290 | Propane | 12 ± 3 | < 0(smog) |
| HC | R-600 | Butane | 12 ± 3 | 0 |
| HC | R-600a | Isobutane | 12 ± 3 | 0[33] |
| HC | R-601 | Pentane | 12 ± 3 | 0 |
| HC | R-601a | Isopentane | 12 ± 3 | 0 |
| HC | R-610 | Ethoxyethane (Diethyl ether) | 12 ± 3 | < 0(smog) |
| HC | R-611 | Methyl formate | 12 ± 3 | 0[33] |
| HCC | R-20 | Chloroform (Trichloromethane) | 0.51 | |
| HCC | R-30 | Dichloromethane (Methylene chloride) | 0.38 | 0 |
| HCC | R-40 | Chloromethane | 1 | 0.02 |
| HCFC | R-21 | Dichlorofluoromethane | 1.7 | 0.04 |
| HCFC | R-22 | Chlorodifluoromethane | 12 | 0.05 |
| HCFC | R-31 | Chlorofluoromethane | 0.02 | |
| HCFC | R-401A | R-22/152a/124 (53±2/13+.5,-1.5/34±1) | 8.514 | 0.034 |
| HCFC | R-401B | R-22/152a/124 (61±2/11+.5,-1.5/28±1) | 9.098 | 0.037 |
| HCFC | R-401C | R-22/152a/124 (33±2/15+.5,-1.5/52±1) | 7.186 | 0.028 |
| HCFC | R-402A | R-125/290/22 (60±2/2±1/38±2) | 22.2 | 0.019 |
| HCFC | R-402B | R-125/290/22 (38±2/2±1/60±2) | 18.46 | 0.03 |
| HCFC | R-403A | R-290/22/218 (5+.2,-2/75±2/20±0) | 529.6 | 0.038 |
| HCFC | R-403B | R-290/22/218 (5+.2,-2/56±2/39±0) | 1,021.32 | 0.028 |
| HCFC | R-405A | R-22/152a/142b/C318 (45±0/7±1/5.5±1/42.5±2) | 1,366.48 | 0.026 |
| HCFC | R-406A | R-22/600a/142b (55±2/4±1/41±0) | 14.419 | 0.056 |
| HCFC | R-406B | R-22/600a/142b (65±2/4±1/31±0) | 13.829 | 0.054 |
| HCFC | R-408A | R-125/143a/22 (7±2/46±1/47±2) | 31.59 | 0.024 |
| HCFC | R-409A | R-22/124/142b (60±2/25±2/15±1) | 11.335 | 0.046 |
| HCFC | R-409B | R-22/124/142b (65±2/25±2/10±1) | 11.04 | 0.045 |
| HCFC | R-412A | R-22/218/142b (70±2/5±2/25±1) | 142.875 | 0.053 |
| HCFC | R-414A | R-22/124/600a/142b (51±2/28.5±2/4±.5/16.5+.5,–1) | 11.2065 | 0.043 |
| HCFC | R-414B | R-22/124/600a/142b (50±2/39±2/1.5±.5/9.5+.5,–1) | 10.1425 | 0.04 |
| HCFC | R-415A | R-22/152a (82±1/18±1) | 10.092 | 0.041 |
| HCFC | R-415B | R-22/152a (25±1/75±1) | 4.05 | 0.013 |
| HCFC | R-416A | R-134a/124/600 (59+.5,–1/39.5+1,–.5/1.5+1,–.2) | 10.731 | 0.009 |
| HCFC | R-418A | R-290/22/152a (1.5±.5/96±1/2.5±.5) | 11.735 | 0.048 |
| HCFC | R-420A | R-134a/142b (88+1,–0/12+0,–1) | 14.468 | 0.008 |
| HCFC | R-500 | R-12/152a (73.8/26.2) | 74.1668 | 0.738 |
| HCFC | R-501 | R-22/12 (75/25) | 34 | 0.288 |
| HCFC | R-502 | R-22/115 (48.8/51.2) | 876.256 | 0.25 |
| HCFC | R-503 | R-23/13 (40.1/59.9) | 491.63 | 0.599 |
| HCFC | R-504 | R-32/115 (48.2/51.8) | 882.962 | 0.228 |
| HCFC | R-505 | R-12/31 (78/22) | 78.0836+ | 0.784 |
| HCFC | R-506 | R-31/114 (55.1/44.9) | 134.90938+ | 0.46 |
| HCFC | R-509 | R-22/218 (44/56) | 1,461.28 | 0.022 |
| HCFO | R-411A | R-1270/22/152a (1.5+0,–1/87.5+2,–0/11+0,–1) | 10.834 | 0.044 |
| HCFO | R-411B | R-1270/22/152a (3+0,–1/94+2,–0/3+0,–1) | 11.682 | 0.047 |
| HCFO | R-411C | R-1270/22/152a (3+0,–1/95.5+2,–0/1.5+0,–1) | 11.841 | 0.048 |
| HFC | R-23 | Trifluoromethane (Fluoroform) | 270 | 0 |
| HFC | R-32 | Difluoromethane | 4.9 | 0 |
| HFC | R-41 | Fluoromethane | 2.4 | 0 |
| HFC | R-263 | Trifluoropropane | 0 | |
| HFC | R-272 | Difluoropropane | 0 | |
| HFC | R-281 | Fluoropropane | 0 | |
| HFO | R-455A | R-1234yf/32/744 (75.5%/21.5%/3%) | ||
| HFO | R-513A | R-1234yf/134a (56%/44%) | 0[31] | |
| HFO | R-1132a | 1,1-Difluoroethylene | 0 | |
| HFO | R-1141 | Fluoroethylene (vinyl fluoride) | 0 | |
| HFO | R-1234yf | 2,3,3,3-Tetrafluoropropene | 0.03012 | 0[33] |
| HFO | R-1234ze | 1,3,3,3-Tetrafluoropropene | 0[33] | |
| HO | R-432A | R-1270/E170 (80±1/20±1) | 9.603 | <0(smog) |
| HO | R-433A | R-1270/290 (30±1/70±1) | 12 ± 3 | < 0(smog) |
| HO | R-433B | R-1270/290 (5±1/95±1) | 12 ± 3 | < 0(smog) |
| HO | R-433C | R-1270/290 (25±1/75±1) | 12 ± 3 | < 0(smog) |
| HO | R-1150 | Ethene (Ethylene) | 12 ± 3 | < 0(smog) |
| HO | R-1270 | Propene (Propylene) | 12 ± 3 | < 0(smog) |
| PCC | R-10 | Carbon tetrachloride (Tetrachloromethane) | 26 | 0.73 |
| PCC | R-110 | Hexachloroethane | ||
| PFC | R-14 | Tetrafluoromethane | 50,000 | 0 |
| PFC | R-116 | Hexafluoroethane | 10,000 | 0 |
| PFC | R-218 | Octafluoropropane | 2,600 | 0 |
| PFC | R-C318 | Octafluorocyclobutane (Perfluorocyclobutane) | 3,200 | 0 |
| PFC | R-3-1-10 | Decafluorobutane (Perfluorobutane) | 2,600 | 0 |
| PFC | R-4-1-12 | Dodecafluoropentane (Perfluoropentane) | 4,100 | 0 |
| PFC | R-5-1-14 | Tetradecafluorohexane (Perfluorohexane) | 3,200 | 0 |
| PFO | R-1114 | Tetrafluoroethylene | 0 | |
| PFO | R-1216 | Hexafluoropropylene | 1,000 | 0 |
| PFO | R-1218 | Hexafluoropropene trimer | 0 |